Type K thermocouples are among the most popular and versatile types of thermocouples. They are used in various industries and applications to measure temperature with a wide temperature range. In this blog, we will discuss everything you need to know about type K thermocouples, including their definition, temperature ranges, accuracy, uses, and more.
What Is a Type K Thermocouple?
A type K thermocouple is a heat sensor whose conducting wires are made from two dissimilar alloys, chromel and alumel, and meet at the junction (the type K thermocouple is one of the “base metal” thermocouples — as opposed to “noble metal” thermocouples).
The thermocouple works based on the Seebeck effect, which states that when two different metals are joined at two different temperatures, a voltage is generated. The voltage produced is proportional to the temperature difference between the two junctions.
What Are the Typical Color Codes for Type K Thermocouples?

Identifying thermocouple types without any technical experience or manual can be challenging, and that’s where the use of color codes comes in. Thermocouples can be easily placed by the color of the jacket covering the wires.
There are two main color codes for type K thermocouples based on the design and performance standards. The positive wire, which is the chromel alloy, is color-coded yellow. The negative wire (alumel alloy) is color-coded red per ANSI/ASTM standards. For IEC-standard type K thermocouples, the positive conductor is colored green and the negative white.
These color codes are not always final because certain manufacturers have their preferences, and the industry in which they will be used may require slight modifications in appearance. You should always double-check with the manual provided by the manufacturer for optimum usage.
Type K Temperature Ranges
Type K thermocouples are accurate over a wide temperature range; they can accurately measure between a low of -200°C to 1260°C (-328°F to 2300°F). However, the maximum continuous temperature for type K thermocouples depends on the insulation material used. PVC insulation has a maximum continuous temperature of 70°C (160°F), while fiberglass insulation can handle up to 260°C (500°F). Compacted mineral insulation can withstand temperatures up to 1200°C (2200°F) in reducing atmospheres. They are relatively inexpensive and reliable in a wide range of settings, which makes them the thermocouple of choice for many industries.
Manufacturer’s Factors
- Accuracy of the thermocouple calibration
- Diameters of the conducting wires
- Materials used for compacted mineral insulation
Other Factors
- Presence of electromagnetic interference
- Aging thermocouple conductors
It is important to get outside help from expert technicians to properly calibrate your thermocouple based on your operation requirements, or your temperature measurements may be inaccurate. This is particularly true if you primarily operate below temperatures of 0℃ where the special limits of errors are unspecified.
What Is the Voltage of Type K Thermocouples?
 All thermocouples operate following the same principles of converting the temperature changes between the measurement and reference junctions into electric signals. These current changes increase with wider temperature change margins.
All thermocouples operate following the same principles of converting the temperature changes between the measurement and reference junctions into electric signals. These current changes increase with wider temperature change margins.
The voltage produced by a type K thermocouple is approximately 41μV/°C (24μV/°F) at 0°C (32°F). The voltage increases as the temperature increases.
However, the relationship between the electrical signals and temperature change is not constant. The connection is represented on the lookup table for type K thermocouples, making converting electric signals to temperature more straightforward.
You can go through the Temp-Pro website for a list of the most commonly demanded K type thermocouples and how much they cost. For a more detailed assessment of your needs, you can contact the technical team to assist in picking the ideal solution for your manufacturing needs.
Why Prefer K Type Thermocouples?
Type K thermocouples are widely used in various industries and applications because of their high accuracy, wide temperature range, and low cost. They are particularly suitable for measuring temperatures in reducing atmospheres and in extreme temperature applications.
Even when many technical experts come across other thermocouples that perform just as well for the temperature they regularly operate within, type K thermocouples still come out on top. Here’s why:
- Type K thermocouples do well in harsh conditions and relatively inert environments. For many buyers, this is what sets this type of thermocouple apart from the others.
- They have fast response times.
- Type Ks are inexpensive but reliable.
- Their durability is not in doubt. Their conducting wires maintain their integrity even at extreme temperatures.
- They can be used in both cooling industries and in high-temperature environments and settings.
Composition of K Type Thermocouples
Both thermocouple probes of the type K are special metals (alloys). They are explicitly designed to withstand the temperature-measuring demands in industrial environments. The positive conductor is made from chromel (90% nickel and 10% chromium). In comparison, the negative conductor is made from Alumel (95% nickel, 2% aluminum, 2% manganese, and 1% silicon).
Type K Insulation Material

Type K thermocouples can be insulated using various materials, including PVC, ceramic, and mineral insulation. PVC is the most common insulation material and is suitable for temperatures up to 70°C (160°F). Fiberglass insulation can withstand temperatures up to 260°C (500°F). Compacted mineral insulation is suitable for high-temperature applications and can withstand temperatures up to 1200°C (2200°F) in reducing atmospheres.
Ceramic is the first choice of material because it is pretty lightweight, does not retain heat, and can withstand temperatures at the upper measuring limits. The materials they are made of are pure, making them considerably inert in harsh conditions.
Compacted mineral insulation is made by compressing a mixture of magnesium oxide and aluminum oxide powder into a solid block. The block is then coated with a metal sheath, which protects the thermocouple from external damage and prevents contamination of the process being measured. Compacted mineral insulation is highly resistant to thermal shock and is suitable for applications where the thermocouple is exposed to rapid temperature changes or liquids.
Accuracy Whichever Is Greater
The accuracy of type K thermocouples depends on the tolerance class. The most common tolerance classes are class 1, class 2, and special limits of error.
Class 1 thermocouples have an accuracy of ± 2.2°C or ± 0.75%, whichever is greater.
Class 2 thermocouples have an accuracy of ± 2.2°C or ± 0.75%, whichever is greater.
Special limits of error thermocouples have an accuracy of ± 1°C or ± 0.4%, whichever is greater.
Tolerance Class
The tolerance class of a thermocouple refers to its accuracy. There are various tolerance classes, including class 1, class 2, and special limits of error. The most common tolerance classes for type K thermocouples are class 1 and class 2.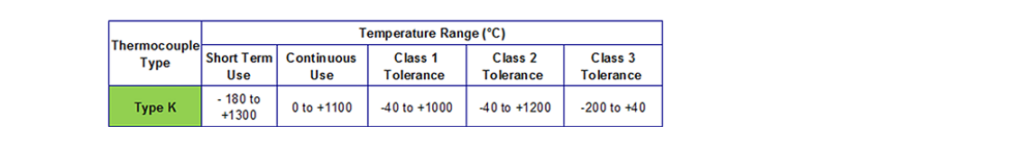
Pros and Cons:
We’ve established why a type K thermocouple may be ideal for your business. They can withstand almost any conditions you throw at them. But before you go with type K, here are some pros and cons you should know.
Pros
- Wide temperature range: Type K thermocouples can measure temperatures ranging from -200°C to 1260°C (-328°F to 2300°F), making them suitable for various applications.
- High accuracy: Type K thermocouples have a high accuracy, making them suitable for applications that require precise temperature measurements.
- Low cost: Type K thermocouples are relatively inexpensive compared to other types of thermocouples.
- Suitable for high-temperature applications: Type K thermocouples are suitable for measuring temperatures in high-temperature applications.
Cons
- Poor stability at high temperatures: Type K thermocouples can experience drift at high temperatures, which can affect their accuracy.
- Limited lifespan: Type K thermocouples have a limited lifespan compared to other types of thermocouples, especially in high-temperature applications.
- Not suitable for vacuum conditions as chromium can be vaporized.
- They experience the green rot phenomenon.
- They are not suitable for a reducing atmosphere nor for a sulfuric atmosphere.
Uses of K Type Thermocouple
Thermocouples are used in several applications. Read this article for a quick rundown of the different thermocouple types and their uses, but here are uses for type K thermocouples.
- Industrial: Type K thermocouples are used in the manufacturing industry to measure temperature in processes such as heat treating, forging, and casting.
- Scientific: Type K thermocouples are used in scientific applications such as laboratory experiments, research, and development.
- Medical: Type K thermocouples are used in medical applications such as monitoring temperature during surgeries and in clinical research.
- Used for testing the safety of heat appliances.
- Used in nuclear applications because they are less susceptible to radiation.
- Used to monitor temperature changes in stainless steel industries.
Takeaways
- Type K thermocouples are versatile and may be the most suitable choice for your temperature monitoring needs.
- The resistance chart should be of little concern to you.
- Type K thermocouples can be stable but react in sulfuric and reducing conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What temp is a type K thermocouple rated for?
Type K thermocouples are suitable for measuring temperatures ranging from -200°C to 1260°C (-328°F to 2300°F). However, the maximum continuous temperature depends on the insulation material used. PVC insulation has a maximum continuous temperature of 70°C (160°F), while fiberglass insulation can handle up to 260°C (500°F). Compacted mineral insulation can withstand temperatures up to 1200°C (2200°F) in reducing atmospheres.
What are K vs. T type thermocouples?
K and T type thermocouples are two different types of thermocouples. K type thermocouples are made from chromel and alumel, while T type thermocouples are made from copper and constantan. K type thermocouples have a wider temperature range (-200°C to 1260°C), while T type thermocouples have a narrower temperature range (-200°C to 350°C). K type thermocouples are more commonly used in industrial and scientific applications, where a wider temperature range is required. T type thermocouples, on the other hand, are commonly used in applications that require precise temperature measurements in a narrow temperature range, such as food processing and HVAC systems. When selecting a thermocouple type, it is important to consider the temperature range and accuracy required for the specific application.
However, type T thermocouples do not offer the same coverage at low temperatures as type K thermocouples. Here’s an extensive guide to help you.
Temp-Pro Holds the Key to All Your Thermocouple Needs
Temp-Pro has been at the forefront of providing thermocouple solutions for businesses for the last half-century. They provide the best services possible, thanks to their team of technical experts and responsive customer care.
What are your thermocouple needs? Tried other solutions that never fit into your production setup? Temp-Pro has the most reliable thermocouples in store and after-service that Fortune 500 companies would envy. Contact Temp-Pro at (800)-991-9093 for a quote today.



