In the highly specialized field of industrial temperature measurement, achieving accuracy is a complex endeavor, demanding both precision and reliability. At Temp-Pro, with decades of expertise since 1972, we specialize in producing advanced temperature sensors, particularly focusing on the nuanced differences between Wire Wound and Thin Film Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs). This technical analysis aims to dissect these two RTD types, providing in-depth insights for industrial professionals seeking the most suitable temperature measurement solutions.
Resistance elements are the core of Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs.) They come in many types conforming to different standards and are capable of measuring different temperature ranges. A bare resistance element is too fragile and sensitive to be used in its raw form necessitating its safeguarding through integration into an RTD. Wire wound vs Thin film – both RTDs function in the same manner: each has a pre-specified resistance value at a known temperature which changes in a predictable fashion.
Composition and Construction Variance
Wire Wound RTDs
Characterized by their construction, these RTDs feature a fine platinum wire, typically 99.99% pure, wrapped around a ceramic or glass core, ensuring minimal thermal conductivity interference. The intricate wire winding pattern is designed to maximize the effective surface area, enhancing the accuracy of temperature measurement, particularly in environments subject to extreme temperatures ranging from -200°C to +850°C.
Thin Film RTDs
These RTDs consist of a platinum-based thin film, often only a few micrometers thick, deposited onto a ceramic substrate through advanced physical vapor deposition techniques. This film is then laser-etched to create an accurate electrical circuit pattern, ensuring consistent resistance characteristics. The thin film’s minimized mass allows for rapid thermal response, typically within the temperature range of -70°C to +500°C.
Temperature Coefficient and Sensitivity Analysis
Wire Wound RTDs
These RTDs stand out for their high temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR), typically around 3850 ppm/K, which translates to enhanced sensitivity and accuracy, particularly crucial in applications requiring precise measurement over a wide temperature gradient. Wire-wound RTDs are the most accurate type of RTD.
Thin Film RTDs
While they offer a slightly lower TCR compared to wire wound types, thin film RTDs still maintain a robust TCR (Temperature Coefficient of Resistance) value, generally around 3750 ppm/K. This characteristic ensures reliable and consistent temperature measurements within their operational temperature range. This variety of RTD is well-received due to its durability, dependability, and low cost. Thin-film elements exhibit heightened resistance to shock or vibration damage compared to other RTD types. Their sleek profile offers design versatility, allowing application across various industrial control and instrumentation scenarios.
Mechanical Stability and Environmental Suitability
Wire Wound RTDs
Owing to their robust construction, involving glass or ceramic housings, these RTDs exhibit superior resistance to environmental stresses, including vibrations, which is essential in heavy industrial settings or applications involving mechanical movement.
Thin Film RTDs
While somewhat less resilient to extreme mechanical stress compared to wire wound types, thin film RTDs are still adequately durable. Their construction includes a protective glass coating, which shields the thin film layer from environmental factors, albeit with a slightly reduced vibration resistance.
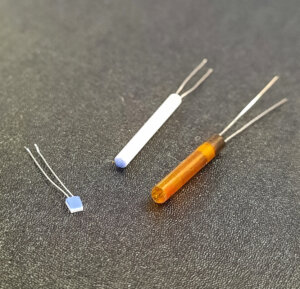
Dimensional Constraints and Installation
Wire Wound RTD
The more complex assembly of wire wound RTDs results in a larger form factor, which might necessitate careful consideration during installation, particularly in space-constrained environments.
Thin Film RTDs
These RTDs are designed for compactness, offering greater flexibility in installation, especially in applications with limited space. Their reduced size does not compromise their operational efficiency, making them suitable for smaller-scale industrial equipment.
Economic Implications and Application Suitability
Wire Wound RTDs
The intricate manufacturing process of wire wound RTDs typically incurs higher costs. This investment is justified for projects that demand high precision across broad temperature ranges, particularly in critical industrial processes.
Thin Film RTDs
Offering a more cost-effective solution, thin film RTDs balance performance with affordability. They are ideal for applications requiring dependable temperature measurements but are constrained by budget considerations.
To conclude, the selection between Wire Wound and Thin Film RTDs hinges on specific industrial requirements, balancing factors like temperature range, precision, mechanical resilience, and economic feasibility. Temp-Pro’s extensive experience and technical prowess in RTD manufacturing ensure we provide the most suitable solutions for your industrial temperature measurement needs. We encourage professionals to explore our diverse range of RTDs and engage with our experts for tailored guidance. For detailed technical support or to discuss specific requirements, please contact one of our experts. Partner with Temp-Pro for unparalleled precision and effectiveness in your temperature control initiatives.



